ISB Journal of Science
Volume 8
January - December, 2014
Archived under the ISJOS collection
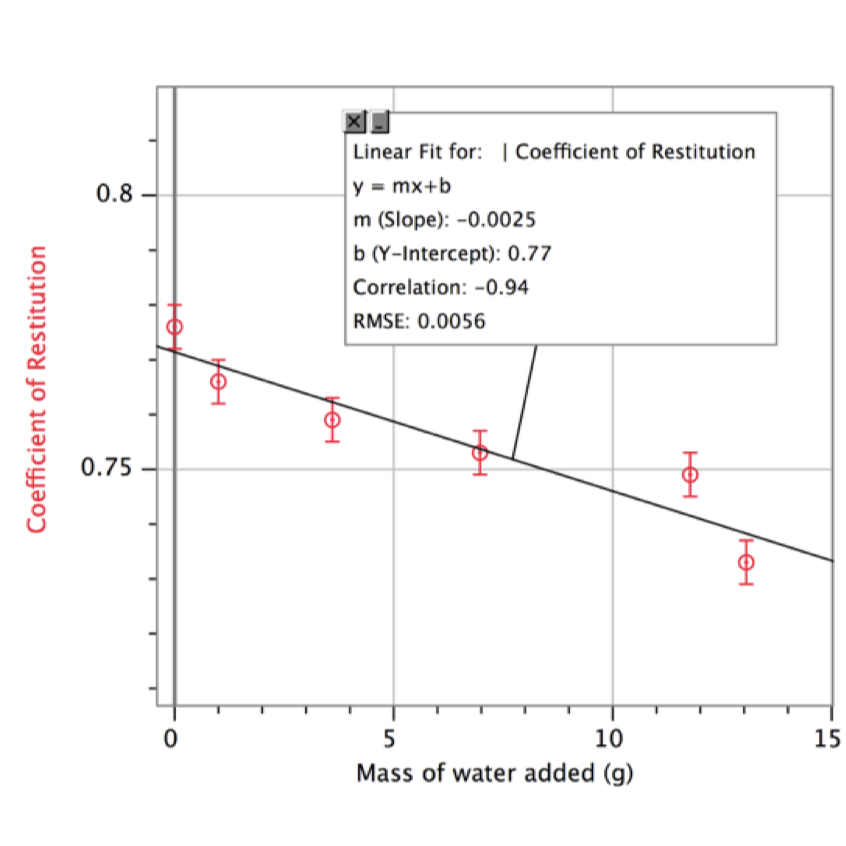
The coefficient of restitution of a damp tennis ball is of interest to tennis players. Using a spray bottle, water was added to a tennis ball and the mass of water on the wet ball was determined. The ball was then dropped from a fixed height of 0.86 m. The motion was recorded with a video camera and the bounce height was measured. Using the bounce height and the original height, the coefficient of restitution for that mass of added water was determined. The research found the mass of water added to the tennis ball to have a negatively linear relationship with the coefficient of restitution of the tennis ball.
Article 2
Sound Quality and Striking Position of a Conga Drum
by Dylan Harvey and Tyler Colton Whiteley

Article 2
Sound Quality and Striking Position of a Conga Drum
by Dylan Harvey and Tyler Colton Whiteley
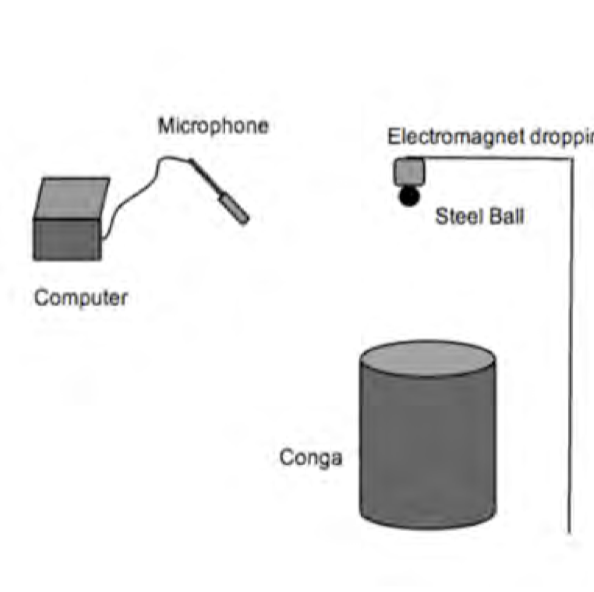
The relationship between the location at which a drum membrane was struck and the quality of sound produced was investigated by striking the drum at several distances between the center and the rim. Through analyzing the harmonics of the wave produced from the impact, it was shown that as the striking location changes, the relative amplitudes of different modes of vibration also changes. It was found that sound of a higher pitch is produced at the rim of the drum than anywhere else on the drum head due to higher modes of vibration becoming dominant.
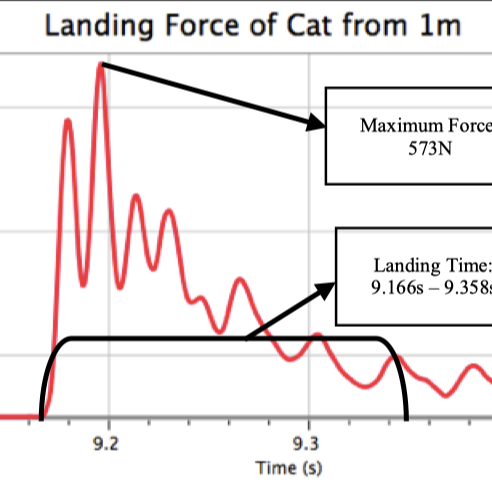
The impact force patterns of a cat landing from various heights were investigated. The cat was dropped onto a force plate from heights ranging between 0.20 and 1.00 m. It was found that the relationship between the cat’s maximum force of impact and its drop height was much lower than would be expected for an inanimate object of similar mass and consistency. The cat clearly manipulated the way in which it landed in order to reduce its impact force. It was also shown that the cat landed one foot at a time, with a consistent force and timing pattern.

Article 4
The Effect of Height, Wing Length, and Wing Symmetry on Tabebuia rosea Seed Dispersal
by Yasmeen Moussa, Sarah Ohashi, and Shawnie Wen

Article 4
The Effect of Height, Wing Length, and Wing Symmetry on Tabebuia rosea Seed Dispersal
by Yasmeen Moussa, Sarah Ohashi, and Shawnie Wen
The relationship between the vertical drop height and the horizontal distance travelled (dispersal ratio) was investigated for a sample of fifty Tabebuia rosea seeds by dropping the seeds from five heights ranging from 1.00 to 2.00 meters. The dispersal ratio was found to be a constant 0.16 m/m for these heights. The effects of total seed length and asymmetry of seed wings on dispersal ratio were also measured using separate samples of fifty Tabebuia rosea seeds. It was found that neither seed length nor asymmetry had a significant effect on the dispersal ratio.
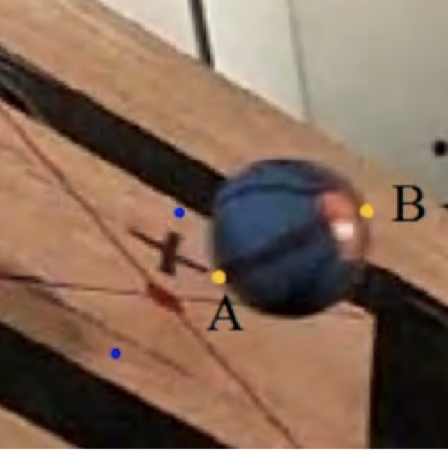

The relationship between the impact angle of a racquetball and the resulting angular velocity of the ball was investigated. Impact angles ranging from 0° to 80° were tested. The ball was dropped at constant speed on a plywood board that could be angled and the impact was filmed at 600 fps. The video was then analyzed to determine the angular velocity of the ball after the bounce. It was found that there is a proportional relationship between the incoming impact angle (θ) and angular velocity (ω) of the racquetball, for angles up to 50°, indicating that the ball did not slip during impact at these angles.
